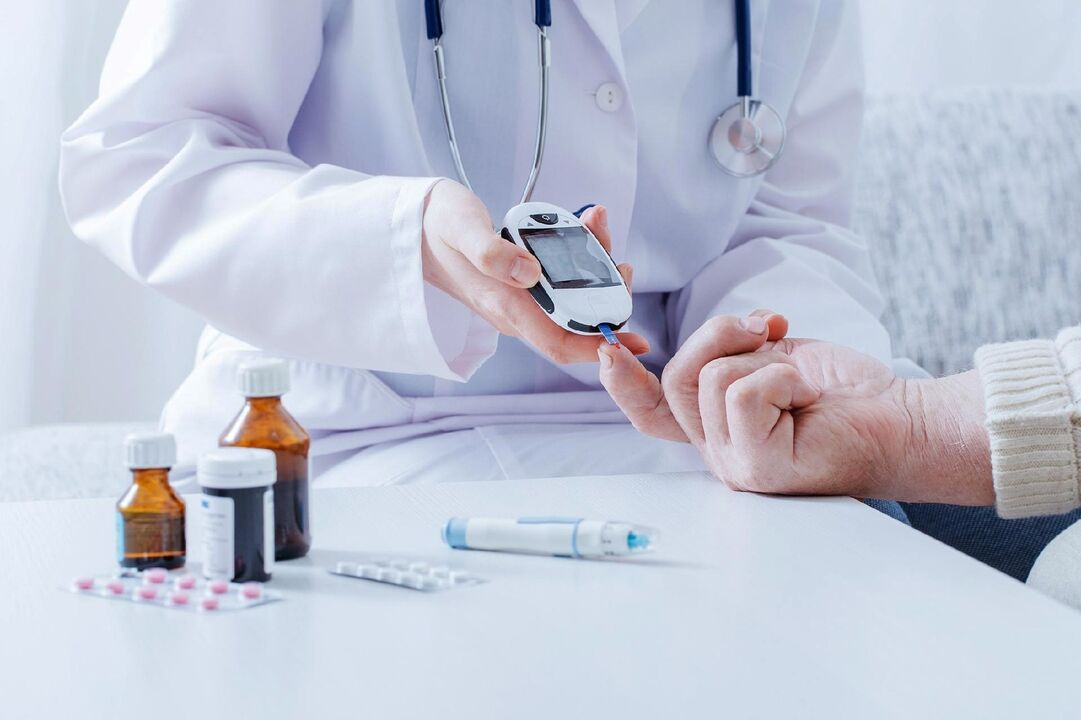
Diabetes. . . Many have heard this word and know that "this disease is somehow related to sugar". Some people are afraid of getting sick, others don't care.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus is a group of endocrine diseases that develop as a result of insufficiency of the hormone insulin, which results in the development of hyperglycemia - a persistent increase in blood glucose levels.
The disease is characterized by a chronic course and disruption of all types of metabolism: carbohydrates, fats, proteins, minerals and water-salt. There are 2 types, each of which requires a special approach.
How do I know if I have diabetes?
Of course, the most accurate diagnostic methods are various blood and urine tests. A one-time sugar measurement is not enough, so if there is any doubt, the doctor will definitely prescribe a series of tests that the patient should undergo.
What could cause such doubts? The main symptoms are:
- Increased urine output caused by an increase in urine pressure due to dissolved glucose in the urine (normally there is no glucose in the urine). It is manifested by frequent, copious urination, including at night.
- Constant unquenchable thirst is caused by significant losses of water in the urine and increased osmotic blood pressure.
- Constant insatiable hunger. This symptom is caused by a metabolic disorder in diabetes, that is, the inability of cells to absorb and process glucose in the absence of insulin (starvation in the midst of plenty).
- Weight loss (especially typical for type 1 diabetes) is a common symptom of diabetes, which develops despite the increased appetite of patients.
Therefore, if you notice these symptoms, consult a doctor immediately!
What are the types of diabetes?
There are a number of classifications of diabetes mellitus according to different criteria. The main types of diabetes include type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is a disease in which the pancreas is unable to produce insulin, which is responsible for the body's absorption of sugar, the so-called insulin-dependent type. As a rule, it is diagnosed in people younger than 30 years old. Such patients are forced to receive insulin artificially (through constant injections).
Type 2 diabetes accounts for 85-90% of all cases of diabetes in adults and is most common among people over the age of 40; usually accompanied by obesity. It is especially important for such patients, as well as people who have a family member with diabetes, to control their blood sugar levels.
The situation is complicated by the fact that, unlike type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes appears gradually. You can be sick for a long time without even realizing it. Often, a person finds out about his illness by accident, during an examination for a completely different reason.
Is there a risk group?
Yes, of course it is. Type 1 diabetes is most often hereditary. The risk also increases with inflammation of the pancreatic tissue, after injuries and infections.
People at risk of developing type 2 diabetes are those whose parents had obesity and/or type 2 diabetes.
How to calculate whether you are at risk of developing diabetes? It is necessary to measure the circumference of the waist and hips, divide the first indicator by the second. If the resulting value is greater than 0. 95 for men and 0. 85 for women, then you are at risk.
What complications does diabetes cause?
The main cause of chronic complications in diabetes is damage to small blood vessels and the peripheral nervous system. The walls of blood vessels and nerves suffer from excess blood sugar; penetrating into them, glucose turns into substances that are toxic to those tissues. As a result, changes occur that disturb the normal functioning of the organ, which has many small vessels and nerve endings. If the patient maintains blood sugar within acceptable limits (6. 7-8. 0 mmol/l), late diabetic complications do not occur.
The negative effects of diabetes have a strong impact on some organs and less on others, for example:
- Eyes - the retina is affected, diabetes can cause cataracts (clouding of the lens) and blindness (retinal changes).
- Teeth - all diseases in the oral cavity develop at an accelerated pace due to the lack of blood supply. There are frequent cases of diabetes being discovered in the doctor's office, where the patient comes with complaints of swollen gums and loose teeth.
- Heart - affected by diabetes; changes in the heart muscle, changes in blood vessels due to high cholesterol lead to coronary disease.
- Liver - when diabetes is poorly compensated, its normal functioning is disturbed and the liver enlarges.
- The kidneys are directly affected by diabetes, resulting in diabetic nephropathy.
- Reproductive system. Diabetes in men leads to impotence in women, miscarriages, premature birth and intrauterine death of the fetus are possible.
- The process of pregnancy and childbirth is very complicated for diabetic women. Pregnant women suffering from diabetes mellitus require the mandatory supervision of two specialists - an endocrinologist and an obstetrician.
- Legs and feet - suffer from diabetes due to damage to blood vessels and nerves. Possible results are trophic ulcers, gangrene, loss of limbs. In addition, feet and nails are susceptible to fungal diseases.
- Joints are more susceptible to processes such as salt deposition than those of a healthy person; in addition, diabetic changes in the joints are possible.
- Diabetes directly affects the circulatory system, which in turn triggers all the above diseases. Blood pressure in diabetics is usually high. Keep in mind that an additional factor that stimulates blood vessel damage in diabetes is smoking.
Therefore, it is important to understand that only by taking control of diabetes and successful compensation can you live a full life. In our country, as in the whole world, many people not only live with diabetes, but also achieve extraordinary successes: they conquer mountain peaks, lead large organizations.
And there is no need to despair if you hear such a diagnosis, everything is in your hands!
Can we cure diabetes?
Unfortunately, scientists have not yet invented a drug that would completely cure a diabetic. Currently, its treatment in most cases is symptomatic and is aimed at removing the symptoms without removing the cause of the disease.
Patient education plays a very important role in diabetes compensation. The patient must understand what diabetes mellitus is, why it is dangerous, what to do in case of sudden changes in blood sugar levels, how to avoid them, be able to independently control blood glucose levels and have a clear understanding of proper nutrition.
Should diabetes be treated?
Undoubtedly! It is important to understand that this disease will not go away on its own. The most important goal in the treatment of diabetes is to constantly monitor blood sugar levels and maintain them at the level recommended by your doctor.
If a person with diabetes approaches this issue responsibly, his health will be the same as that of a healthy person. Moreover, the future prognosis in terms of complications, duration and quality of life will be favorable.
Is it difficult to control your blood glucose level?
In the modern world, this is no longer a problem. If before blood sugar could only be measured in a laboratory, now it is very easy to do it at home. There are high-precision glucometers for measuring glucose. They are compact, very easy to use and designed specifically for independent measurement of glucose levels. If necessary, you can find out your sugar level at home, at work, on a trip, etc.
The whole process takes literally seconds and requires only one drop of blood. The test strip draws a drop and the result appears on the screen.
Prevention of diabetes
You must remember that the best way to protect yourself is constant prevention, which you can do yourself:
- Active lifestyle and weight control. Diabetes is directly related to obesity. Physical activity helps lower blood sugar and reduces the need for insulin.
- Proper nutrition. Eat foods rich in dietary fiber, which normalize bowel function and lower cholesterol levels. These products include all fruits and vegetables, legumes, dairy products, nuts and others.
- Rejection of excessive consumption of flour products, sweets, pasta and pastries. Eat only whole grain bread.
- Avoid stress and don't smoke. One of the causes of diabetes is stress and anxiety. Stress and smoking reduce the body's resistance to diabetes.
- Monitor your blood glucose levels regularly if you are over 40 years old. It is also necessary to make a sugar test for those who tend to be obese and lead a sedentary lifestyle.